Introduction to Rigid PCBs and Flex PCBs
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in modern electronics, providing a platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components. PCBs come in various types, each designed to cater to specific requirements and applications. Two common types of PCBs are Rigid PCBs and Flex PCBs. In this article, we will explore the differences between these two types of PCBs and discuss the advantages and applications of Rigid-flex PCBs, a hybrid combination of both.
What Are Rigid PCBs?
Rigid PCBs, also known as standard PCBs, are the most common type of printed circuit boards. They are made from a solid substrate material, typically FR-4, which is a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. Rigid PCBs are characterized by their rigidity and stability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Characteristics of Rigid PCBs
- Substrate Material: Rigid PCBs use a solid substrate material, usually FR-4, which provides excellent mechanical strength and stability.
- Rigidity: As the name suggests, Rigid PCBs are inflexible and maintain their shape under normal conditions.
- Thickness: Rigid PCBs come in various thicknesses, typically ranging from 0.8mm to 3.2mm, depending on the number of layers and the application requirements.
- Copper Layers: Rigid PCBs can have multiple copper layers, ranging from single-layer to multi-layer designs, allowing for complex routing and high component density.
- Solder Mask and Silkscreen: Rigid PCBs are often coated with a solder mask to protect the copper traces and prevent short circuits. They also feature silkscreen printing for component identification and assembly instructions.
Advantages of Rigid PCBs
- Durability: Rigid PCBs are robust and can withstand mechanical stress, making them suitable for applications that require high reliability and long-term use.
- High Component Density: With the ability to accommodate multiple layers and fine-pitch components, Rigid PCBs allow for high component density and complex designs.
- Excellent Thermal Management: The solid substrate material of Rigid PCBs provides good thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat dissipation from components.
- Cost-effective: Rigid PCBs are relatively inexpensive to manufacture, especially in large quantities, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Applications of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs find applications in a wide range of industries and products, including:
- Consumer electronics (smartphones, tablets, laptops)
- Industrial control systems
- Automotive electronics
- Medical devices
- Telecommunications equipment
- Aerospace and defense systems

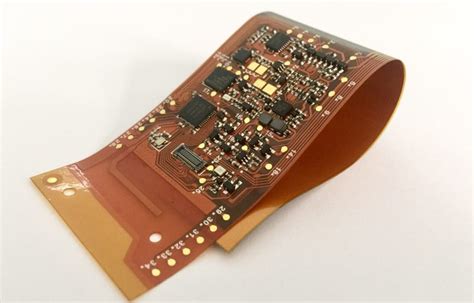
What Are Flex PCBs?
Flex PCBs, short for Flexible Printed Circuit Boards, are a type of PCB that can bend and flex without damaging the electronic circuits. They are made from flexible substrate materials, such as polyimide or polyester, which allow the PCB to conform to various shapes and fit into tight spaces.
Characteristics of Flex PCBs
- Substrate Material: Flex PCBs use flexible substrate materials, such as polyimide or polyester, which can bend and flex without breaking.
- Flexibility: Flex PCBs are designed to be flexible and can bend, twist, and fold to conform to different shapes and fit into compact spaces.
- Thickness: Flex PCBs are typically thinner than Rigid PCBs, with thicknesses ranging from 0.1mm to 0.3mm.
- Copper Layers: Flex PCBs can have single or multiple copper layers, depending on the design requirements. The copper traces are usually thinner compared to Rigid PCBs to maintain flexibility.
- Coverlay: Instead of a solder mask, Flex PCBs use a coverlay, which is a thin, flexible layer that protects the copper traces and provides electrical insulation.
Advantages of Flex PCBs
- Flexibility and Conformity: Flex PCBs can bend and conform to various shapes, making them ideal for applications with limited space or requiring a custom fit.
- Lightweight and Thin: Due to their thin profile and flexible substrate material, Flex PCBs are lightweight and can be used in applications where weight and size are critical factors.
- Improved Reliability: Flex PCBs eliminate the need for connectors and wires between different parts of the circuit, reducing the risk of connection failures and improving overall reliability.
- Dynamic Flexing: Flex PCBs can withstand repeated bending and flexing, making them suitable for applications that require continuous motion or dynamic flexing.
- Design Freedom: Flex PCBs offer greater design freedom, allowing for unique and creative form factors that would be challenging to achieve with Rigid PCBs.
Applications of Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs are commonly used in applications that require flexibility, compact packaging, or unique form factors, such as:
- Wearable devices (smartwatches, fitness trackers)
- Medical implants and devices
- Aerospace and military equipment
- Automotive electronics (sensors, displays)
- Consumer electronics (cameras, printers)
- Robotics and automation systems

Rigid-Flex PCBs: Combining the Best of Both Worlds
Rigid-Flex PCBs are a hybrid combination of Rigid PCBs and Flex PCBs, offering the benefits of both technologies in a single circuit board. They consist of rigid sections connected by flexible sections, allowing for a unique blend of stability and flexibility.
Characteristics of Rigid-Flex PCBs
- Combination of Rigid and Flexible Sections: Rigid-Flex PCBs have both rigid and flexible sections within the same circuit board. The rigid sections provide stability and support for components, while the flexible sections allow for bending and folding.
- Interconnections: The rigid and flexible sections are interconnected using plated Through-Holes (PTHs) or other methods, ensuring reliable electrical connections between the sections.
- 3D Packaging: Rigid-Flex PCBs enable 3D packaging, where the flexible sections can be folded and shaped to fit into complex or compact spaces.
- Customization: Rigid-Flex PCBs can be customized to meet specific design requirements, with various combinations of rigid and flexible layers, thicknesses, and materials.
Advantages of Rigid-Flex PCBs
- Space Savings: Rigid-Flex PCBs allow for more compact and space-efficient designs by eliminating the need for separate rigid and flexible circuits and reducing the overall package size.
- Reduced Weight: By combining rigid and flexible sections in a single PCB, Rigid-Flex PCBs can reduce the overall weight of the electronic assembly.
- Enhanced Reliability: Rigid-Flex PCBs eliminate the need for connectors and wires between rigid and flexible sections, reducing the potential for connection failures and improving reliability.
- Improved Signal Integrity: The seamless integration of rigid and flexible sections in Rigid-Flex PCBs minimizes signal loss and interference, resulting in better signal integrity compared to separate rigid and flexible circuits.
- Design Flexibility: Rigid-Flex PCBs offer significant design flexibility, allowing for unique and complex form factors that would be difficult to achieve with traditional PCBs.
Applications of Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-Flex PCBs find applications in various industries where space constraints, reliability, and design flexibility are critical factors, such as:
- Aerospace and defense systems
- Medical devices and equipment
- Automotive electronics
- Wearable technology
- Industrial automation and robotics
- High-end consumer electronics

Comparison Table: Rigid PCBs vs. Flex PCBs
| Feature | Rigid PCBs | Flex PCBs |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Material | FR-4 (glass-reinforced epoxy) | Polyimide or polyester |
| Flexibility | Rigid and inflexible | Flexible and can bend or fold |
| Thickness | 0.8mm to 3.2mm | 0.1mm to 0.3mm |
| Copper Layers | Single to multi-layer | Single to multi-layer |
| Protective Layer | Solder mask | Coverlay |
| Durability | High mechanical strength | Can withstand repeated flexing |
| Component Density | High | Moderate to high |
| Thermal Management | Excellent | Limited |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Higher than rigid PCBs |
| Design Freedom | Limited by rigidity | High, enables unique form factors |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, industrial control, automotive, medical, telecommunications, aerospace | Wearable devices, medical implants, aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, robotics |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the main difference between Rigid PCBs and Flex PCBs?
A: The main difference between Rigid PCBs and Flex PCBs is their flexibility. Rigid PCBs are made from a solid substrate material and are inflexible, while Flex PCBs use flexible substrate materials and can bend and conform to various shapes. -
Q: Can Flex PCBs replace Rigid PCBs in all applications?
A: No, Flex PCBs cannot replace Rigid PCBs in all applications. While Flex PCBs offer advantages in terms of flexibility and design freedom, Rigid PCBs are still preferred in applications that require high mechanical strength, thermal management, and cost-effectiveness. -
Q: What are Rigid-Flex PCBs, and what are their advantages?
A: Rigid-Flex PCBs are a hybrid combination of Rigid PCBs and Flex PCBs, featuring both rigid and flexible sections in a single circuit board. They offer advantages such as space savings, reduced weight, enhanced reliability, improved signal integrity, and design flexibility. -
Q: Are Flex PCBs more expensive than Rigid PCBs?
A: Yes, Flex PCBs are generally more expensive than Rigid PCBs due to the specialized materials, manufacturing processes, and design considerations involved. However, the added cost can be justified in applications that require the unique benefits offered by Flex PCBs. -
Q: What are some common applications of Rigid-Flex PCBs?
A: Rigid-Flex PCBs find applications in industries where space constraints, reliability, and design flexibility are critical, such as aerospace and defense systems, medical devices, automotive electronics, wearable technology, industrial automation, and high-end consumer electronics.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Rigid PCBs and Flex PCBs is crucial when designing electronic systems. Rigid PCBs offer durability, high component density, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. On the other hand, Flex PCBs provide flexibility, lightweight design, and unique form factors, catering to applications that require bending or compact packaging.
Rigid-Flex PCBs, a hybrid combination of both technologies, offer the best of both worlds by combining the stability of rigid sections with the flexibility of flexible sections. This enables space savings, enhanced reliability, and improved signal integrity, making Rigid-Flex PCBs an attractive choice for demanding applications.
When selecting between Rigid PCBs, Flex PCBs, or Rigid-Flex PCBs, designers must consider factors such as the application requirements, space constraints, reliability needs, and cost. By understanding the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each type of PCB, designers can make informed decisions and choose the most suitable solution for their specific project.
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for innovative and efficient PCB solutions will continue to grow. Rigid PCBs, Flex PCBs, and Rigid-Flex PCBs will play a crucial role in shaping the future of electronics, enabling the development of more advanced, compact, and reliable devices across various industries.
Leave a Reply