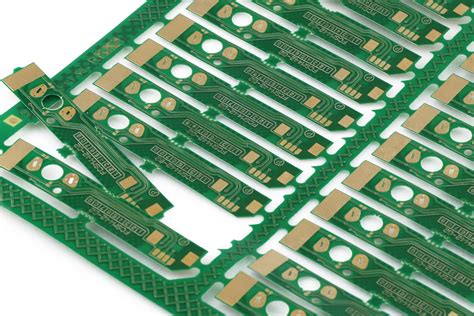
What is Panelization?
Panelization is the process of arranging multiple printed circuit boards (PCBs) on a single panel for manufacturing. This technique is widely used in PCB fabrication to maximize production efficiency and minimize costs. By grouping several PCBs together, manufacturers can produce a larger number of boards in a single run, reducing the overall production time and material waste.
Benefits of Panelization
- Cost reduction: Panelizing PCBs allows for the production of multiple boards in a single run, reducing the cost per board.
- Increased efficiency: Manufacturing panels with multiple PCBs is faster than producing individual boards, as it minimizes the number of setups and changeovers required.
- Improved handling: Panels are easier to handle during the manufacturing process, as they are larger and more stable than individual PCBs.
- Consistent quality: Producing multiple PCBs on a single panel ensures consistent quality across all boards, as they are subjected to the same manufacturing conditions.
Breakaway Tabs and Mouse Bites
To facilitate the separation of individual PCBs from the panel after manufacturing, designers incorporate breakaway tabs or mouse bites into the panelization layout.
Breakaway Tabs
Breakaway tabs, also known as snap-off tabs or break-off tabs, are small, thin sections of the panel that connect individual PCBs to the main panel. These tabs are designed to be easily broken off by hand or with minimal force, allowing for the separation of the individual boards from the panel.
Advantages of Breakaway Tabs
- Easy separation: Breakaway tabs allow for quick and easy separation of individual PCBs from the panel without the need for specialized tools.
- Minimal damage: When designed and manufactured correctly, breakaway tabs minimize the risk of damaging the individual PCBs during the separation process.
- Cost-effective: Breakaway tabs are a simple and cost-effective solution for panelization, as they do not require additional manufacturing steps or materials.
Breakaway Tab Dimensions
The dimensions of breakaway tabs can vary depending on the size and thickness of the PCBs being panelized. However, some general guidelines for designing breakaway tabs include:
| Parameter | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Tab width | 1.0 mm – 2.0 mm |
| Tab length | 2.0 mm – 5.0 mm |
| Tab thickness | 0.5 mm – 1.0 mm |
It is essential to consider the material properties and the specific requirements of the project when determining the appropriate dimensions for breakaway tabs.
Mouse Bites
Mouse bites, also known as perforations or V-grooves, are a series of small, closely spaced holes or slots cut into the panel between individual PCBs. These perforations weaken the panel material, allowing for easy separation of the individual boards by applying minimal force.
Advantages of Mouse Bites
- Cleaner edges: Mouse bites produce cleaner edges on the individual PCBs compared to breakaway tabs, as the perforations guide the separation process.
- Reduced stress: The closely spaced holes or slots distribute the stress evenly along the separation line, reducing the risk of damaging the individual PCBs during the separation process.
- Versatility: Mouse bites can be used with a variety of PCB materials and thicknesses, making them a versatile choice for panelization.
Mouse Bite Dimensions
The dimensions of mouse bites can vary depending on the specific requirements of the project and the capabilities of the manufacturing equipment. Some general guidelines for designing mouse bites include:
| Parameter | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Hole diameter | 0.5 mm – 1.0 mm |
| Hole spacing | 0.5 mm – 1.0 mm |
| Slot width | 0.5 mm – 1.0 mm |
| Slot length | 1.0 mm – 2.0 mm |
| Slot spacing | 0.5 mm – 1.0 mm |
It is crucial to consult with the PCB manufacturer to determine the optimal dimensions for mouse bites based on their equipment and experience.

Panelization Layout Considerations
When designing a panelization layout, there are several factors to consider to ensure the best possible results:
- PCB orientation: Arrange the individual PCBs on the panel in a way that maximizes the number of boards per panel while minimizing material waste.
- Spacing between PCBs: Provide adequate spacing between individual PCBs to accommodate breakaway tabs or mouse bites and to ensure proper separation without damaging the boards.
- Panel border: Include a sufficient panel border around the perimeter of the panel to provide structural stability and to allow for handling during the manufacturing process.
- Fiducial marks: Incorporate fiducial marks on the panel to assist with alignment and registration during the manufacturing process.
- Tooling holes: Include tooling holes in the panel to facilitate handling and alignment during the various stages of manufacturing.
Spacing Between PCBs
The spacing between individual PCBs on a panel is a critical factor in ensuring proper separation and minimizing the risk of damage. The appropriate spacing depends on the chosen separation method (breakaway tabs or mouse bites) and the specific requirements of the project.
For breakaway tabs, a minimum spacing of 2.0 mm to 3.0 mm between PCBs is generally recommended. This spacing allows for the placement of the tabs and provides adequate room for the separation process.
When using mouse bites, the spacing between PCBs can be reduced to 1.0 mm to 2.0 mm, as the perforations require less space than breakaway tabs. However, it is essential to consult with the PCB manufacturer to determine the optimal spacing based on their equipment and experience.
Panel Border
Including a panel border around the perimeter of the panel is essential for several reasons:
- Structural stability: The panel border provides structural support to the panel, preventing warping or damage during handling and manufacturing.
- Handling: The border allows for easier handling of the panel during the manufacturing process, as it provides a surface for gripping and manipulation.
- Labeling: The panel border can be used to include labeling information, such as the project name, revision number, or manufacturing date.
A typical panel border width ranges from 5.0 mm to 10.0 mm, depending on the size of the panel and the specific requirements of the project.

FAQ
-
What is the purpose of panelization in PCB manufacturing?
Panelization allows for the production of multiple PCBs on a single panel, increasing manufacturing efficiency and reducing costs. -
What are breakaway tabs, and how do they work?
Breakaway tabs are small, thin sections of the panel that connect individual PCBs to the main panel. They are designed to be easily broken off by hand or with minimal force, allowing for the separation of the individual boards from the panel. -
What are mouse bites, and how do they differ from breakaway tabs?
Mouse bites are a series of small, closely spaced holes or slots cut into the panel between individual PCBs. They weaken the panel material, allowing for easy separation of the individual boards by applying minimal force. Mouse bites produce cleaner edges on the individual PCBs compared to breakaway tabs. -
What factors should be considered when designing a panelization layout?
When designing a panelization layout, consider factors such as PCB orientation, spacing between PCBs, panel border, fiducial marks, and tooling holes to ensure the best possible results. -
Why is the spacing between PCBs important in panelization?
The spacing between individual PCBs on a panel is critical for ensuring proper separation and minimizing the risk of damage. The appropriate spacing depends on the chosen separation method (breakaway tabs or mouse bites) and the specific requirements of the project. Adequate spacing allows for the placement of tabs or perforations and provides room for the separation process.

Conclusion
Panelization is a crucial technique in PCB manufacturing that enables the production of multiple boards on a single panel, improving efficiency and reducing costs. Breakaway tabs and mouse bites are two common methods for separating individual PCBs from the panel, each with its own advantages and design considerations.
When designing a panelization layout, it is essential to consider factors such as PCB orientation, spacing between PCBs, panel border, fiducial marks, and tooling holes. By carefully planning the layout and consulting with the PCB manufacturer, designers can ensure that the panelized PCBs are produced efficiently and with the highest quality.
As PCB technology continues to advance, the importance of proper panelization techniques will only grow. By understanding the dimensions and design considerations for breakaway tabs and mouse bites, PCB designers can create panelization layouts that maximize manufacturing efficiency and minimize the risk of damage to the individual boards.
Leave a Reply