Importance of a Bill of Materials
1. Accurate Inventory Management
A well-structured BOM list enables companies to maintain accurate inventory levels. By having a clear understanding of the components and materials needed for each product, businesses can optimize their inventory, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. This leads to improved efficiency and cost savings.
2. Cost Control
The BOM list provides a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with each component and material. This information allows companies to identify areas where costs can be reduced, such as sourcing alternative suppliers or negotiating better prices. By closely monitoring the BOM, businesses can effectively manage their production costs and maintain profitability.
3. Efficient Production Planning
A comprehensive BOM list facilitates efficient production planning. It provides a clear roadmap for the manufacturing process, outlining the specific components and materials required at each stage. This information helps in scheduling production activities, allocating resources, and ensuring a smooth flow of materials throughout the production line.
4. Quality Control
The BOM list serves as a reference point for quality control. By specifying the exact components and materials to be used in each product, it ensures consistency and adherence to quality standards. Any deviations from the BOM can be easily identified and rectified, minimizing the risk of defects or product failures.
5. Collaboration and Communication
The BOM list acts as a central document that facilitates collaboration and communication among different departments within an organization. It provides a common language and understanding of the product’s composition, enabling cross-functional teams to work together effectively. This collaboration is crucial for successful product development and launch.
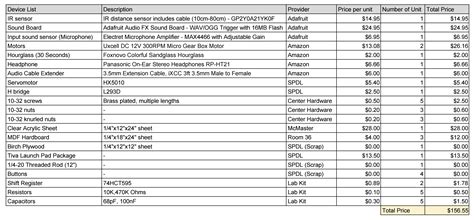
Key Components of a BOM List
A typical BOM list includes the following components:
- Item Number: A unique identifier for each component or material.
- Description: A brief description of the item, including its specifications and characteristics.
- Quantity: The number of units required for each item in the production of one finished product.
- Unit of Measure: The standard unit used to measure the quantity of each item (e.g., pieces, kilograms, meters).
- Part Number: The manufacturer’s or supplier’s part number for each item.
- Reference Designator: A code used to identify the location or placement of each item within the product.
- Level: Indicates the hierarchical level of each item within the BOM structure.
Here’s an example of a simple BOM list for a wooden chair:
| Item No. | Description | Quantity | Unit | Part No. | Ref. Designator | Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wooden Seat | 1 | pc | WS-001 | Seat | 1 |
| 2 | Wooden Leg | 4 | pc | WL-001 | Leg1, Leg2, Leg3, Leg4 | 1 |
| 3 | Wood Screw | 16 | pc | WS-002 | Screw1, Screw2, … | 2 |
| 4 | Wood Glue | 100 | ml | WG-001 | Glue | 2 |

Types of BOM Lists
There are different types of BOM lists, each serving a specific purpose within the production process:
1. Engineering BOM (EBOM)
The Engineering BOM, also known as the Design BOM, is created by the product design team. It includes all the components and materials required to design and develop the product. The EBOM focuses on the functional aspects of the product and may include items that are not necessarily used in the final production.
2. Manufacturing BOM (MBOM)
The Manufacturing BOM is derived from the EBOM and is tailored specifically for the production process. It includes all the components and materials required to physically manufacture the product. The MBOM takes into account any changes or modifications made during the transition from design to production.
3. Sales BOM (SBOM)
The Sales BOM, also known as the Customer BOM, is a simplified version of the BOM that is shared with customers or sales teams. It includes only the high-level components or subassemblies that are relevant to the customer. The SBOM is used for quoting prices, generating sales orders, and communicating product information to customers.
4. Service BOM
The Service BOM is used for after-sales support and maintenance of the product. It includes all the components, spare parts, and consumables required to service and repair the product throughout its lifecycle. The Service BOM is essential for providing effective customer support and ensuring the long-term reliability of the product.

Creating and Managing a BOM List
Creating and managing a BOM list requires a systematic approach and the use of appropriate tools and software. Here are some best practices for effective BOM management:
1. Use a Centralized Database
Maintain a centralized database or system to store and manage all BOM-related information. This ensures data integrity, version control, and easy access for all stakeholders.
2. Standardize Naming Conventions
Establish standardized naming conventions for components, materials, and part numbers. This helps in maintaining consistency and avoiding confusion or duplication.
3. Regularly Review and Update
Regularly review and update the BOM list to reflect any changes in product design, component specifications, or supplier information. This ensures that the BOM remains accurate and up to date.
4. Integrate with Other Systems
Integrate the BOM management system with other key business systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Manufacturing Execution System (MES), and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software. This enables seamless data flow and reduces the risk of errors or discrepancies.
5. Train and Educate
Provide training and education to all relevant personnel on the importance of BOM management and the processes involved. This ensures that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities in maintaining an accurate and up-to-date BOM list.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between a BOM and a parts list?
A BOM is a comprehensive list that includes all the components, materials, and quantities required to manufacture a product. It provides a hierarchical structure and includes information such as part numbers, descriptions, and reference designators. On the other hand, a parts list is a simpler list that includes only the individual components or parts without the detailed structure or hierarchy found in a BOM.
2. How do I create a BOM list?
To create a BOM list, follow these steps:
1. Break down the product into its individual components and subassemblies.
2. Assign unique item numbers and descriptions to each component.
3. Specify the quantity required for each item.
4. Include relevant information such as part numbers, reference designators, and units of measure.
5. Organize the components into a hierarchical structure based on their level within the product.
6. Review and validate the BOM list with cross-functional teams.
7. Enter the BOM information into a centralized database or system for management and maintenance.
3. What software can I use to manage BOM lists?
There are various software solutions available for managing BOM lists, including:
– Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems
– Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software
– Specialized BOM management tools
– Spreadsheet software (e.g., Microsoft Excel)
The choice of software depends on the complexity of your products, the size of your organization, and your specific requirements. It is recommended to use a dedicated BOM management system for efficient and accurate BOM handling.
4. How often should I update my BOM list?
The frequency of updating your BOM list depends on the nature of your products and the dynamics of your business. It is crucial to update the BOM whenever there are changes in product design, component specifications, or supplier information. Regular reviews and updates ensure that the BOM remains accurate and reflects the current state of the product.
5. Can a BOM list be used for multiple products?
Yes, a BOM list can be used for multiple products if they share common components or subassemblies. In such cases, you can create a modular BOM structure where the common components are listed separately and referenced in the BOMs of individual products. This approach helps in standardizing components, reducing duplication, and improving efficiency in BOM management.
Conclusion
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a critical document in the manufacturing process that lists all the components, parts, and materials required to produce a product. It serves as a foundation for accurate inventory management, cost control, efficient production planning, quality control, and collaboration among different departments.
Creating and managing a BOM list requires a systematic approach, the use of appropriate tools and software, and adherence to best practices such as maintaining a centralized database, standardizing naming conventions, regularly reviewing and updating the BOM, integrating with other systems, and providing training to relevant personnel.
By implementing an effective BOM management system, companies can streamline their production processes, reduce errors and inefficiencies, and ultimately improve their bottom line. The BOM list is not just a simple document but a powerful tool that enables businesses to optimize their operations and deliver high-quality products to their customers.
Leave a Reply