RF & Microwave Blog
-
 Read more: Sealed lead acid battery charging circuit diagram
Read more: Sealed lead acid battery charging circuit diagramIntroduction to SLA Batteries and Charging Circuits Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) batteries are a popular choice for various applications due to their reliability, low maintenance, and cost-effectiveness. These batteries are commonly used in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), emergency lighting systems, security systems, and even in some automotive applications. To ensure […]
-
 Read more: Uyemura to Provide Solutions to eSurface Licensees
Read more: Uyemura to Provide Solutions to eSurface LicenseesUyemura-eSurface Partnership Expands Innovative Plating Technologies Uyemura International Corporation, a global leader in advanced plating technologies, has announced a strategic collaboration with eSurface Technologies to provide comprehensive solutions to eSurface licensees. This partnership aims to revolutionize the electronics manufacturing industry by combining Uyemura’s expertise in high-performance plating chemistries with eSurface’s […]
-
FR 4 PCB material with TG
Posted by
–
 Read more: FR 4 PCB material with TG
Read more: FR 4 PCB material with TGWhat is FR4-TG? FR4-TG is a high-performance printed circuit board (PCB) material that belongs to the FR-4 family of glass-reinforced epoxy laminate materials. The “TG” in FR4-TG stands for “Tg,” which represents the glass transition temperature of the material. FR4-TG is designed to offer enhanced thermal stability and improved mechanical […]
-
QFN and QFP what service to use HASL or ENIG
Posted by
–
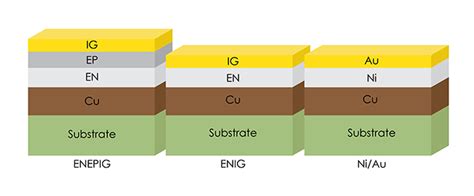 Read more: QFN and QFP what service to use HASL or ENIG
Read more: QFN and QFP what service to use HASL or ENIGIntroduction to QFN and QFP Packages Quad Flat No-lead (QFN) and Quad Flat Package (QFP) are two of the most commonly used surface-mount package types in modern electronic devices. These packages offer several advantages, including smaller footprints, better thermal and electrical performance, and lower costs compared to traditional through-hole packages. […]
-
High Current PCB designing
Posted by
–
 Read more: High Current PCB designing
Read more: High Current PCB designingIntroduction to High Current PCB Design Printed circuit boards (PCBs) that carry high currents require special design considerations to ensure reliable operation and prevent issues such as overheating, voltage drop, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). High current PCBs are used in a variety of applications including power supplies, motor controllers, automotive […]
-
 Read more: What is UL certification and How to mark it on the circuit board
Read more: What is UL certification and How to mark it on the circuit boardIntroduction to UL Certification UL (Underwriters Laboratories) is a global safety certification company that tests and certifies products to ensure they meet rigorous safety standards. UL certification is a widely recognized mark of safety compliance for electrical and electronic products, including printed circuit boards (PCBs). Obtaining UL certification for your […]
-
AOI in PCB and SMT Production Line
Posted by
–
 Read more: AOI in PCB and SMT Production Line
Read more: AOI in PCB and SMT Production LineIntroduction to AOI in PCB and SMT Manufacturing Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) is a crucial quality control process in the production of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly lines. AOI systems utilize advanced imaging technology and software algorithms to detect defects, ensure proper component placement, and […]
-
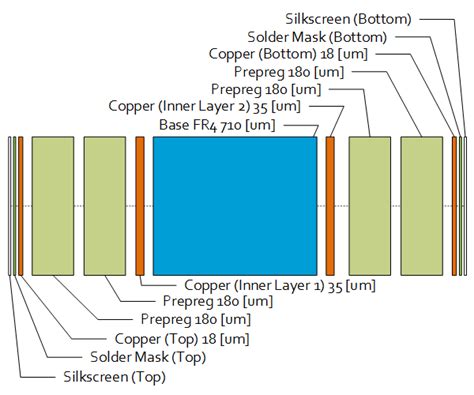 Read more: Some PCB Design Guidelines You Need to Know An Advise From a PCB Engineer
Read more: Some PCB Design Guidelines You Need to Know An Advise From a PCB EngineerUnderstand the Importance of PCB Design Guidelines PCB design guidelines are a set of rules and best practices that help designers create printed circuit boards that meet the required specifications and perform optimally. These guidelines cover various aspects of PCB design, including component placement, routing, signal integrity, power distribution, and […]
-
What is surface mount technology SMT
Posted by
–
 Read more: What is surface mount technology SMT
Read more: What is surface mount technology SMTHistory of Surface-Mount Technology The origins of SMT can be traced back to the 1960s when IBM introduced the first surface-mount package for their System/360 mainframe computer. However, it wasn’t until the 1980s that SMT gained widespread adoption in the electronics industry. The introduction of smaller, more compact components and […]
-
What is PCB File
Posted by
–
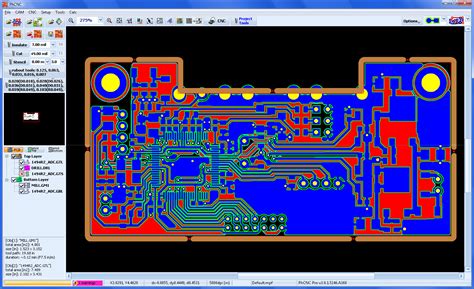 Read more: What is PCB File
Read more: What is PCB FileIntroduction to PCB Files A PCB file, short for Printed Circuit Board file, is a digital document that contains all the necessary information and data required to design and manufacture a printed circuit board. PCB files are created using specialized software tools known as EDA (Electronic Design Automation) or ECAD […]
Recent Posts
- How to Select Material for Your PCBs from Cost and Reliability Considerations
- Problems of EMC Technology Application in PCB Design of Electronic Devices and the Strategies
- Fabrication Technology on Flex-Rigid PCB Window
- Problems of High-Frequency and High-Speed Multilayer PCB Fabrication and Their Solutions
- Key Difficulties and Tips for Backplane PCB Fabrication