
RF & Microwave Blog
-
RAYPCB Certificate of IATF
Posted by
–
 Read more: RAYPCB Certificate of IATF
Read more: RAYPCB Certificate of IATFWhat is IATF Certification? The International Automotive Task Force (IATF) is a group of automotive manufacturers and their respective trade associations, formed to provide improved quality products to automotive customers worldwide. The IATF 16949 standard, developed by the IATF, is a global technical specification and quality management standard for the […]
-
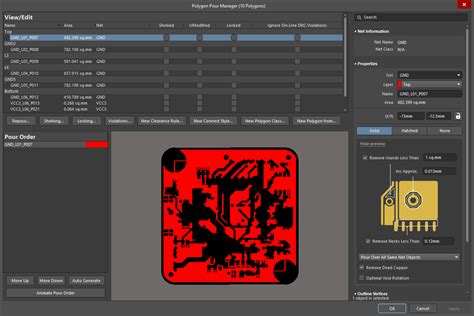 Read more: Altium Polygon pour breaks on rigid flex split lines
Read more: Altium Polygon pour breaks on rigid flex split linesUnderstanding the Polygon Pour Issue in Altium Designer When designing rigid-flex PCBs in Altium Designer, a common issue arises with polygon pour breaks along the split lines between the rigid and flexible sections. This problem can lead to inconsistencies in the copper distribution, potentially affecting the electrical performance and manufacturability […]
-
Audio low noise preamplifier circuit diagram
Posted by
–
 Read more: Audio low noise preamplifier circuit diagram
Read more: Audio low noise preamplifier circuit diagramKey Components of an Audio Preamplifier The main components of a typical audio preamplifier include: Input stage: This is where the low-level audio signal enters the preamplifier. It usually includes input jacks, switching for multiple sources, and sometimes a phono preamp for turntables. Gain stage: This is the heart of […]
-
 Read more: How to make a construction process of open source ergonomic Keyboard PCB project
Read more: How to make a construction process of open source ergonomic Keyboard PCB projectIntroduction to Open-Source Ergonomic Keyboard PCBs Ergonomic keyboards have gained popularity among computer users due to their ability to reduce strain and improve typing comfort. While commercial ergonomic keyboards are readily available, many enthusiasts prefer to design and build their own custom keyboards using open-source PCB (Printed Circuit Board) designs. […]
-
 Read more: Multilayer PCB board material prepreg key performance indicators
Read more: Multilayer PCB board material prepreg key performance indicatorsImportance of Prepreg in Multilayer PCBs Multilayer PCBs have become increasingly popular in the electronics industry due to their ability to accommodate complex circuitry and high component density in a compact form factor. The use of prepreg is essential in the construction of these multilayer boards, as it serves several […]
-
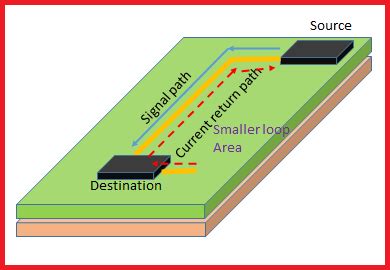 Read more: Using Return Paths that Follow Least Impedance to create a better PCB Design
Read more: Using Return Paths that Follow Least Impedance to create a better PCB DesignUnderstanding Least-Impedance Return Paths In the world of PCB design, creating efficient and reliable return paths is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices. One key concept that designers must grasp is the idea of least-impedance return paths. By understanding and implementing this principle, designers can create PCBs […]
-
 Read more: Top 7 Most Common Gerber File Mistakes and How to Avoid Them RAYPCB
Read more: Top 7 Most Common Gerber File Mistakes and How to Avoid Them RAYPCB1. Incorrect File Format One of the most common mistakes designers make is saving their Gerber files in the wrong format. PCB fabrication houses typically require Gerber files to be in the RS-274X format, also known as Extended Gerber or X2 format. This format includes aperture definitions and other essential […]
-
Purple color solder mask PCB
Posted by
–
 Read more: Purple color solder mask PCB
Read more: Purple color solder mask PCBIntroduction to Purple PCBs Purple PCBs, also known as purple solder mask PCBs, have gained popularity in recent years due to their unique aesthetic appeal and functional benefits. These printed circuit boards feature a distinctive purple color on the solder mask layer, which not only adds visual interest but also […]
-
 Read more: PCB Design Software The First Step to a New PC Board
Read more: PCB Design Software The First Step to a New PC BoardIntroduction to PCB Design Printed Circuit Board (PCB) design is a crucial step in the development of electronic devices. It involves creating a layout of electronic components and the connections between them on a board. The PCB design process can be complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized knowledge and tools. This […]
-
PCB manufacturer in India
Posted by
–
 Read more: PCB manufacturer in India
Read more: PCB manufacturer in IndiaOverview of the PCB Industry in India The Indian PCB industry has witnessed significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand from various sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunications, and aerospace. The government’s initiatives to promote electronics manufacturing, such as the “Make in India” campaign and the […]
Recent Posts
- How to Select Material for Your PCBs from Cost and Reliability Considerations
- Problems of EMC Technology Application in PCB Design of Electronic Devices and the Strategies
- Fabrication Technology on Flex-Rigid PCB Window
- Problems of High-Frequency and High-Speed Multilayer PCB Fabrication and Their Solutions
- Key Difficulties and Tips for Backplane PCB Fabrication